SSD (solid-state drive)
What is an SSD?
An SSD, or solid-state drive, is a type of storage device used in computers. This non-volatile storage media stores persistent data on solid-state flash memory. SSDs replace traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) in computers and perform the same basic functions as a hard drive. But SSDs are significantly faster in comparison. With an SSD, the device's operating system will boot up more rapidly, programs will load quicker and files can be saved faster.
A traditional hard drive consists of a spinning disk with a read/write head on a mechanical arm called an actuator. An HDD reads and writes data magnetically. The magnetic properties, however, can lead to mechanical breakdowns.
By comparison, an SSD has no moving parts to break or spin up or down. The two key components in an SSD are the flash controller and NAND flash memory chips. This configuration is optimized to deliver high read/write performance for sequential and random data requests.
SSDs are used anywhere that hard drives can be deployed. In consumer products, for example, they are used in personal computers (PCs), laptops, computer games, digital cameras, digital music players, smartphones, tablets and thumb drives. They are also incorporated with graphics cards. However, they are more expensive than traditional HDDs.

Businesses with a rapidly expanding need for higher input/output (I/O) have fueled the development and adoption of SSDs. Because SSDs offer lower latency than HDDs, they can efficiently handle both heavy read and random workloads. That lower latency stems from the ability of a flash SSD to read data directly and immediately from stored data.
High-performance servers, laptops, desktops or any application that needs to deliver information in real-time can benefit from solid-state drive technology. Those characteristics make enterprise SSDs suitable to offload reads from transaction-heavy databases. They can also help to alleviate boot storms with virtual desktop infrastructure, or inside a storage array to store frequently used data locally using a hybrid cloud.
How do SSDs work?
An SSD reads and writes data to underlying interconnected flash memory chips made out of silicon. Manufacturers build SSDs by stacking chips in a grid to achieve different densities.
SSDs read and write data to an underlying set of interconnected flash memory chips. These chips use floating gate transistors (FGTs) to hold an electrical charge, which enables the SSD to store data even when it is not connected to a power source. Each FGT contains a single bit of data, designated either as a 1 for a charged cell or a 0 if the cell has no electrical charge.
Every block of data is accessible at a consistent speed. However, SSDs can only write to empty blocks. And although SSDs have tools to get around this, performance may still slow over time.
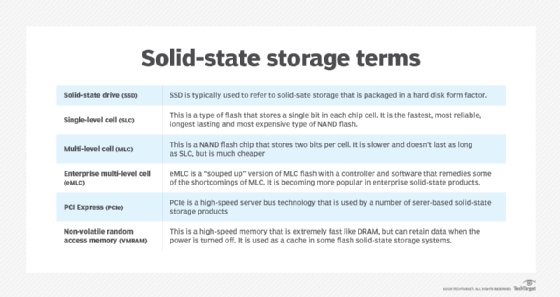
SSDs use three main types of memory: single-, multi- and triple-level cells. Single-level cells can hold one bit of data at a time -- a one or zero. Single-level cells (SLCs) are the most expensive form of SSD, but are also the fastest and most durable. Multi-level cells (MLCs) can hold two bits of data per cell and have a larger amount of storage space in the same amount of physical space as a SLC. However, MLCs have slower write speeds. Triple-level cells (TLCs) can hold three bits of data in a cell. Although TLCs are cheaper, they also have slower write speeds and are less durable than other memory types. TLC-based SSDs deliver more flash capacity and are less expensive than an MLC or SLC, albeit with a higher likelihood for bit rot due to having eight states within the cell.
What are the major features of SSDs?
Several features characterize the design of an SSD. Because it has no moving parts, an SSD is not subject to the same mechanical failures that can occur in HDDs. SSDs are also quieter and consume less power. And because SSDs weigh less than hard drives, they are a good fit for laptop and mobile computing devices.
In addition, the SSD controller software includes predictive analytics that can alert a user in advance of a potential drive failure. Because flash memory is malleable, all-flash array vendors can manipulate the usable storage capacity using data reduction techniques.
What are the advantages of SSDs?
The benefits of SSDs over HDDs include:
- Faster read/write speeds. SSDs can access large files quickly.
- Quicker boot times and better performance. Because the drive does not need to spin up as an HDD would, it is more responsive and provides better load performance.
- Durability. SSDs are more shock-resistant and can handle heat better than HDDs because they do not have moving parts.
- Power consumption. SSDs need less power to operate than HDDs due to their lack of moving parts.
- Quieter. SSDs produce less audible noise because there are no moving or spinning parts.
- Size. SSDs come in a variety of form factors whereas HDD sizes are limited.
What are the disadvantages of SSDs?
Downsides that come with SSDs include:
- Cost. SSDs are more expensive than traditional HDDs.
- Life expectancy. Some SSDs, for example, those using NAND memory-flash chips, can only be written a specified number of times that is typically less than HDDs.
- Performance. Limitations on the number of write cycles cause SSDs to decrease in performance over time.
- Storage options. Because of cost, SSDs are typically sold in smaller sizes.
- Data recovery. This time-consuming process can be expensive, as the data on damaged chips may not be recoverable.
What are the types of SSD non-volatile memory?
NAND and NOR circuitry differ in the type of logic gate they use. NAND devices use eight-pin serial access to data. Meanwhile, NOR flash memory is commonly used in mobile phones, supporting 1-byte random access.
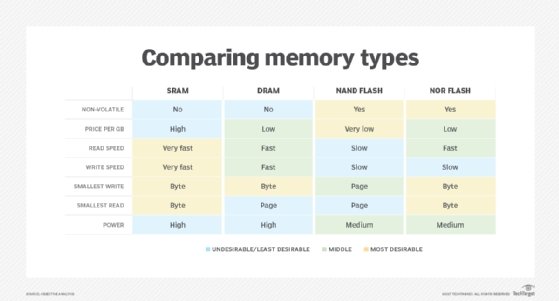
Compared with NAND, NOR flash offers fast read times, but is generally a more expensive memory technology. NOR writes data in large chunks, meaning it takes longer to erase and write new data. The random-access capabilities of NOR are used for executing code, while NAND flash is intended for storage. Most smartphones support both types of flash memory, using NOR to boot up the operating system and removable NAND cards to expand the device's storage capacity.
What are the types of SSDs?
Types of SSDs include:
- Solid-state drives. Basic SSDs deliver the least performance. SSDs are flash devices that connect via Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) or serial-attached SCSI (SAS) and provide a cost-effective first step into the solid-state world. For many environments, the performance boost in sequential read speeds from a SATA or SAS SSD will suffice.
- PCIe-based flash. Peripheral Component Interconnect Express-based flash is the next step up in performance. While these devices typically offer greater throughput and more input/output operations per second, the biggest advantage is significantly lower latency. The downside is that most of these offerings require a custom driver and have limited built-in data protection.
- Flash DIMMs. Flash dual in-line memory modules reduce latency, going further than PCIe flash cards by eliminating the potential PCIe bus contention. They require custom drivers unique to flash DIMMS, with specific changes to the read-only I/O system on the motherboard.
- NVMe SSDs. These SSDs use the non-volatile memory express (NVMe) interface specification. This accelerates data transfer speeds between client systems and solid-state drives over a PCIe bus. NVMe SSDs are designed for high-performance non-volatile storage and are well-suited for highly demanding, compute-intensive settings.
- NVMe-oF. The NVMe over Fabrics protocol enables data transfers between a host computer and a target solid-state storage device. NVMe-oF transfers data through methods such as Ethernet, Fibre Channel or InfiniBand.
- Hybrid DRAM-flash storage. This dynamic random access memory (DRAM) channel configuration combines flash and server DRAM. These hybrid flash storage devices address the theoretical scaling limit of DRAM and are used to increase throughput between application software and storage.
SSD form factors
SSD manufacturers offer diverse form factors. The most common form factor is a 2.5-inch SSD that is available in multiple heights and supports SAS, SATA and NVMe protocols.
The Solid State Storage Initiative, a project of the Storage Networking Industry Association, identified the following three major SSD form factors:
- SSDs that come in traditional HDD form factors and fit into the same SAS and SATA slots in a server.
- Solid-state cards that use standard add-in card form factors, such as those with a PCIe serial port card. A PCIe-connected SSD does not require network host bus adapters to relay commands, which speeds the performance of storage. These devices include the U.2 SSDs that are generally considered the eventual replacement for drives used in thin laptops.
- Solid-state modules that reside in a DIMM or small outline dual in-line memory module. They may use a standard HDD interface such as SATA. These devices are known as non-volatile DIMM (NVDIMM) cards.
Two types of RAM are used in a computer system: DRAM, which loses data when power is lost, and static RAM. NVDIMMs provide the persistent storage a computer needs to recover data. They place flash close to the motherboard, but operations are carried out in DRAM. The flash component fits into a memory bus for backup on high-performance storage.
Both SSDs and RAM incorporate solid-state chips, but the two memory types function differently within a computer system.
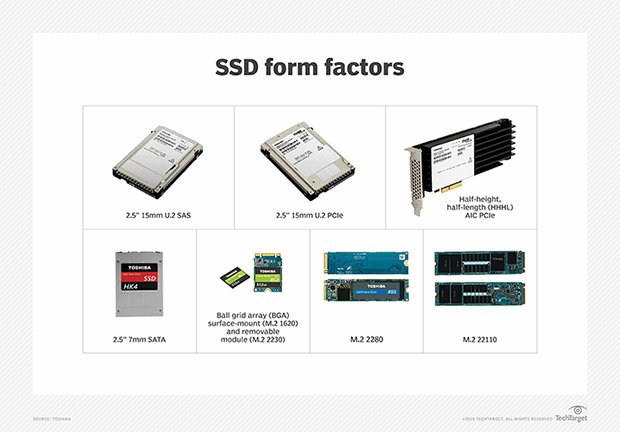
Two newer form factors worth noting are M.2 and U.2 SSDs. An M.2 SSD varies in length -- typically from 42 millimeters (mm) to 110 mm -- and attaches directly to a motherboard. It communicates via NVMe or SATA. The small size of an M.2 limits the surface area for heat dissipation which, over time, will reduce its performance and stability. In enterprise storage, M.2 SSDs often are used as a boot device. In consumer devices, such as notebook computers, an M.2 SSD provides capacity expansion.
A U.2 SSD describes a 2.5-inch PCIe SSD. These small form-factor devices were formerly known as SFF-8639. The U.2 interface enables high-speed NVMe-based PCIe SSDs to be inserted in a computer's circuit board, without the need to power down the server and storage.
SSD manufacturers
The SSD market is dominated by a handful of large manufacturers, including:
- Crucial
- Intel
- Kingston Technology
- Micron Technology Inc.
- Samsung
- SanDisk
- Seagate Technology
- SK Hynix
- Western Digital Corp.
These manufacturers produce and sell NAND flash chipsets to solid-state drive vendors. They also market branded SSDs based on their own flash chips. Factors to consider when shopping for SSDs include:
- Durability. Every SSD warranty covers a finite number of drive cycles, determined by the type of NAND flash. An SSD used only for reads does not require the same level of endurance as an SSD intended to handle mostly writes.
- Form factor. This determines if a replacement SSD works with existing storage and the number of SSDs that can fit in a single chassis.
- Interface. This determines maximum throughput and minimum latency thresholds, as well as the expansion capabilities of the SSD. Manufacturers qualify their SSDs for NVMe, SAS and SATA.
- Power usage. The drive interface also specifies the maximum power of an SSD, although many enterprise SSDs are engineered to be tuned while in operation.
Historically, SSDs cost more than conventional hard drives. But due to improvements in manufacturing technology and expanded chip capacity, SSD prices had been dropping, enabling consumers and enterprise customers to view SSDs as a viable alternative to conventional storage. However, prices are increasing due to chip shortages and a general volatile market -- more recently in 2020 and 2021, due to COVID-19-related supply chain issues. Fluctuating demand for flash chips has kept pricing for SSDs variable, but the price for an SSD remains higher than an HDD.
SSD vs. HDD
SSDs are considered much faster than the highest performing HDDs. Latency is also substantially reduced, and users typically experience much faster boot times.
Several factors influence the lifespan of SSDs and HDDs, including heat, humidity and the effect of metals oxidizing inside the drives. Data on both types of media will degrade over time, with HDDs generally supporting a higher number of drive writes per day. Industry experts recommend storing unused or idle SSDs at low temperatures to extend their life.
The moving parts of HDDs increase the chance of failures. To compensate, HDD manufacturers have added shock sensors to protect drives and other components inside PCs. This type of sensor detects if the machine is about to fall and takes steps to shut down the HDD and related critical hardware.
Read performance of an HDD can suffer when data is split into different sectors on the disk. To repair the disk, a technique known as defragmentation is used. SSDs do not store data magnetically, so the read performance remains steady, regardless of where the data is stored on the drive.
SSDs have a set life expectancy, with a finite number of write cycles before performance becomes erratic. To compensate, SSDs employ wear leveling, a process that extends the life of an SSD. Wear leveling is typically managed by the flash controller, which uses an algorithm to arrange data so write/erase cycles are distributed evenly among all the blocks in the device. Another technique, SSD overprovisioning, can help minimize the impact of garbage collection write amplification.
SSD vs. eMMC
An embedded MultiMediaCard (eMMC) provides the onboard flash storage in a computer. It is installed directly on the computer motherboard. The architecture includes NAND flash memory and a controller designed as an integrated circuit. EMMC storage is typically found in cellphones, less expensive laptops and IoT applications.
An eMMC device delivers performance roughly equivalent to that of an SSD. But they differ in capacity, as a standard eMMC typically ranges from 1 GB to 512 GB, and SSD sizes can range from 128 GB to multiple terabytes. This makes eMMCs best suited for handling smaller file sizes.

In portable devices, an eMMC serves as primary storage or as an adjunct to removable SD and microSD multimedia cards. Although this is the historical use of eMMC devices, they are increasingly deployed in sensors inside connected internet of things devices.
SSD vs. hybrid hard drive
Although not as widely used as a standard solid-state drive, an alternative is a hybrid hard drive (HHD). HHDs bridge the gap between flash and fixed-disk magnetic storage and are used to upgrade laptops, both for capacity and performance.
HHDs have a conventional disk architecture that adds approximately 8 GB of NAND flash as a buffer for disk-based workloads.
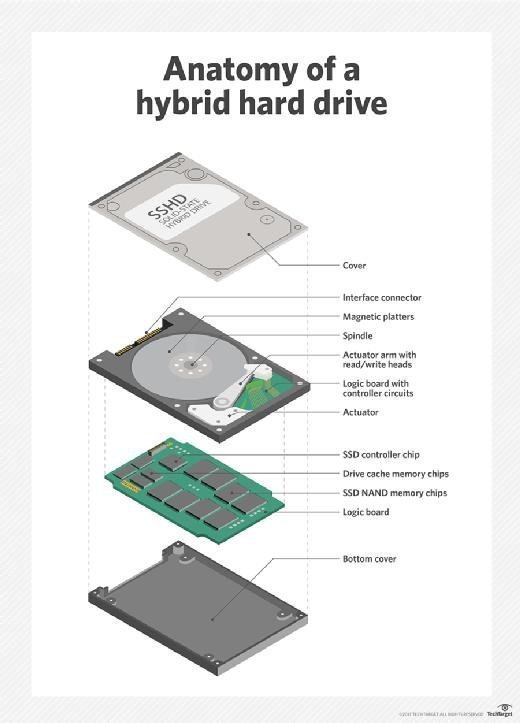
As such, an HHD is best suited for computers with a limited number of applications. The cost of a hybrid hard drive is slightly less than an HDD.
History and evolution of SSDs
The earliest solid-state drives generally were designed for consumer devices. This changed in 1991 when SanDisk released the first commercial flash-based SSD. Commercially designed SSDs were made with enterprise multi-level cell flash technology, which enhanced write cycles.
Other notable dates include:
- The debut of the Apple iPod in 2005 marked the first notable flash-based device to broadly penetrate the consumer market.
- Toshiba announced 3D V-NAND in 2007. 3D flash devices boost capacity and performance.
- EMC -- now Dell EMC -- is credited with being the first vendor to include SSDs in enterprise storage hardware, adding the technology to its Symmetrix disk arrays in 2008. This spawned the creation of hybrid flash arrays that combine flash drives and HDDs.
- Toshiba introduced triple-level cells in 2009. TLC flash is a type of NAND flash memory that stores three bits of data per cell.
- IBM is considered the first major storage vendor to release a dedicated all-flash array platform, called FlashSystem, based on technology from its acquisition of Texas Memory Systems in 2012. Around that time, Nimbus Data, Pure Storage, Texas Memory Systems and Violin Memory began pioneering the adoption of all-flash arrays, relying on SSD storage to replace hard disks.
- In 2012, EMC acquired XtremIO and now ships an all-flash system based on the XtremIO technology.
Learn more about four causes of SSD failure and best practices for dealing with them in this article.







