eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard)
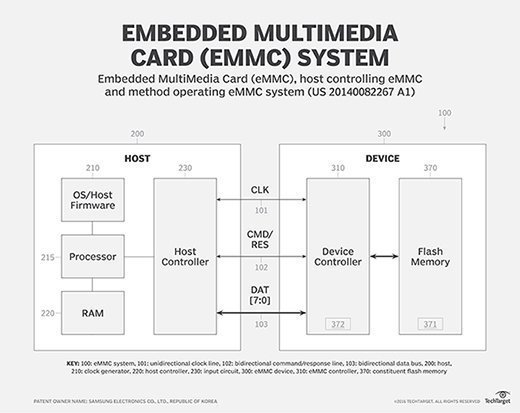
An embedded MultiMediaCard (eMMC) is a small storage device made up of NAND flash memory and a simple storage controller. The eMMC standard for embedded flash memory applications was developed in 2006 by JEDEC and the MultiMediaCard Association.
The technology is intended for use in portable devices such as cell phones and, more recently, for sensors connected to the Internet of Things (IoT). Both the flash memory and controller are contained on a single integrated circuit (IC) that is embedded permanently into a device.
An eMMC acts as the primary storage for portable devices like cell phones or tablets, which can augment that storage with a removable Secure Digital card or microSD multimedia card. It is the sole storage for very small sensors connected to IoT. The connection to the main board of the device is parallel, but the latest eMMC specification (version 5.1) allows for a transfer rate up to 400 megabytes per second (MBps), which is comparable to a solid-state drive using a SATA connection.
Use cases for eMMC
The primary user of eMMC has been the mobile device industry, which uses the technology in cell phones, tablets and notebooks. The largest capacity eMMC available is 128 gigabytes (GB); it is made by Samsung and used in lightweight notebook computers. As the IoT has become more common, the sensors built into the devices that collect data and return that data to a business or organization have relied on smaller eMMC integrated circuits.

In addition, eMMCs have become increasingly used in the automobile industry, as more vehicles have onboard entertainment or navigation systems. Companies such as SanDisk have introduced ruggedized eMMCs to stand up to the environmental and stress demands of industrial and automotive use. However, these come with a price premium.
The eMMC IC is attached through a parallel connection directly to the main circuit board of whatever device for which it stores data. By using an integrated controller in the eMMC, the device CPU no longer has to handle placing data into storage since the controller in the eMMC takes over that function., This frees up the CPU -- a lower speed, lower power chip than ones used in PCs or servers -- for more important tasks. By using flash memory, the entire IC-based storage draws little power as compared to a spinning disk.
UFS: Replacement for eMMC
In 2011, JEDEC released the Universal Flash Storage (UFS) standard, intended to replace both eMMC and SD flash memory cards with a single standard. In February 2015, Samsung announced its first UFS embedded memory for portable devices, in sizes up to 128 GB. In July 2016, Samsung announced its first removable SD cards based on UFS.







