
SSD form factor
What is an SSD form factor?
An SSD form factor is the size, configuration or physical arrangement of solid-state storage media. The form factor determines the media's physical compatibility and interchangeability with other computer components or devices.
The Storage Networking Industry Association has identified three major form factors for the enterprise: solid-state drives (SSDs), solid-state cards and solid-state modules.
SSDs come in traditional hard disk drive (HDD) form factors and fit into the same slots. Solid-state cards use standard card form factors, such as Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe), also known as PCI Express, and reside on a printed circuit board.
Solid-state modules reside in a dual in-line memory module or small outline DIMM. They may use a standard HDD interface, such as Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA).
A fourth form factor, the portable USB drive, is generally considered to be consumer solid-state storage.
How do SSD form factors work?
Computer systems use two types of RAM. Dynamic RAM (DRAM) requires power to function and loses its data when power shuts down. Static RAM (SRAM) holds an electric charge to keep data ready for use. Both types of RAM can be implemented on an SSD form factor and connector, and both support a variety of storage device types.
Form factors can be designed for insertion into the drive bay of a storage device, such as the motherboard in a laptop computer. They can also be plugged into the USB port of a laptop or other computing device. The application for an SSD determines the form factor used.
The form factor describes the physical shape and configuration of the SSD unit. It can be configured in different ways and may include SRAM, DRAM, flash memory, a bus to connect each component, various controllers and connectors for plugging the device into a motherboard or a USB port. Components that may appear in a form factor include PCIe SSDs, SATA SSDs and M.2 SSDs, as well as non-volatile memory express, or NVMe, SSD technology devices and an operating system.

Types of form factors
SSDs are typically based on flash memory. Flash retains data for a period of time if the power is off and comes in different sizes. As a result, various form factors are available for SSDs.
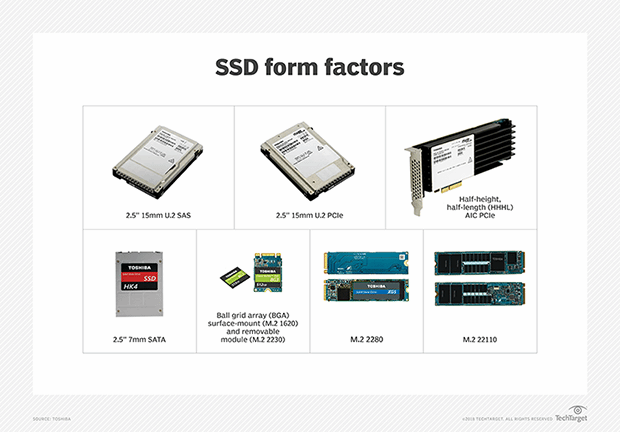
The following is a list of the primary form factor types:
- Enterprise and Data Center Standard Form Factor (EDSFF). A consortium of vendors developed the EDSFF set of specifications. EDSFF variants share the same operating protocol, interface, connector and pin configuration.
- M.2. Previously known as Next Generation Form Factor, or NGFF, M.2 form factor SSDs are internally mounted. It supports various interfaces, comes in different sizes, is smaller than the 2.5-inch SSD form factor and typically is removable.
- U.2. This form factor has a 2.5-inch width and a 3.6-inch length. U.2 comes in two different thicknesses: 7 millimeter and 15 mm. It is a widely used SSD form factor, supports multiple interfaces and is typically implemented in systems that are built around HDDs.
- Add-in cards. These are plugged into a system's drive bay and have an external faceplate that is typically screwed into the device housing alongside other similar cards. Add-in cards are used in situations that need high-performance computational and storage resources.
Learn more about common SSD form factors and flash memory in this comprehensive guide.







