InfiniBand
What is InfiniBand?
InfiniBand is an industry standard communications specification the InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA) developed. The specification defines a switched fabric architecture for interconnecting servers, communications infrastructure equipment, storage and embedded systems in the data center.
InfiniBand is known for its high performance and low latency. A connection that supports a 4x link width can deliver up to 400 gigabits per second throughput. There are plans for faster speeds in the future. InfiniBand is also highly scalable. It can support tens of thousands of nodes in a single subnet. It provides quality of service (QoS) and failover capabilities that make it well suited to high-performance computing (HPC) environments.
InfiniBand is one of the network fabrics that the non-volatile memory express over fabrics (NVMe-oF) storage protocol uses. NVMe-oF also runs over Ethernet, Fibre Channel (FC) and TCP/IP networks.
How does InfiniBand work?
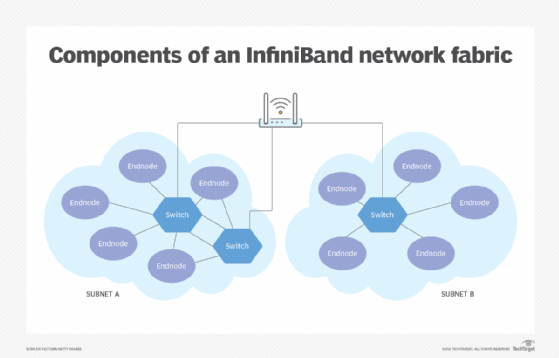
InfiniBand is a channel-based fabric that facilitates high-speed communications between interconnected nodes. An InfiniBand network is typically made up of processor nodes, such as PCs, servers, storage appliances and peripheral devices. It also has network switches, routers, cables and connectors.
Each processor node is configured with a host channel adapter, and each peripheral device has a target channel adapter. InfiniBand adheres to a channel model similar to that used by many mainframe computers. All transmissions begin or end with a channel adapter. These adapters can exchange information that ensures security or works with a given QoS level.
In an InfiniBand network, data is transmitted in packets that are organized into messages. InfiniBand is a messaging service that can be used by a range of high-performing applications, such as data mining, deep learning and predictive analytics. InfiniBand supports the following types of communication messages:
- remote direct memory access read or write operations;
- channel send or receive messages;
- Multicast transmissions; and
- reversible transaction-based operations.
The InfiniBand architecture specification was developed by merging two competing designs:
- Future I/O, developed by Compaq, Hewlett-Packard and IBM; and
- Next Generation I/O, developed by Intel, Microsoft and Sun Microsystems.
IBTA is responsible for maintaining and enhancing the specification.
What are the benefits of InfiniBand?
InfiniBand offers a range of benefits, including the following:
Faster and efficient. The internal data flow system in many PCs and servers is inflexible and relatively slow. As the amount of data coming into and flowing between components in the computer increases, the existing bus system becomes a bottleneck. Most of these systems send data in parallel across the backplane bus. However, InfiniBand uses serial links and buses to send data one bit at a time, resulting in faster and more efficient communication.
Less expensive and reliable. InfiniBand connections also require fewer pins and other electrical connections, cutting manufacturing costs and improving reliability. In addition, the serial bus can carry multiple channels of data at the same time in a multiplexing signal. InfiniBand also supports multiple memory areas, each of which can be addressed by both processors and storage devices.
High throughput and low latency. Because of its architecture, InfiniBand delivers exceptional throughput and low latency. It is well suited for performance-sensitive application environments, such as HPC and supercomputers. The architecture's low processing overhead also reduces the reliance on central processing unit resources and frees them up for other operations.
Supports high-performance workloads. InfiniBand is a mature technology. It provides an efficient, reliable and stable environment for supporting high-performance workloads.
Scalability. It also offers a relatively simple and highly scalable architecture. Not only can it support thousands of nodes within a single subnet, but it can also be extended through InfiniBand routers to create nearly unlimited cluster sizes.
Management flexibility. The InfiniBand specification standardizes the management infrastructure, making it possible to control the InfiniBand environment through existing enterprise management tools.
Find out the differences among various networking fabrics, including Ethernet, FC and InfiniBand.








