NVMe over Fibre Channel (NVMe over FC) or FC-NVMe standard
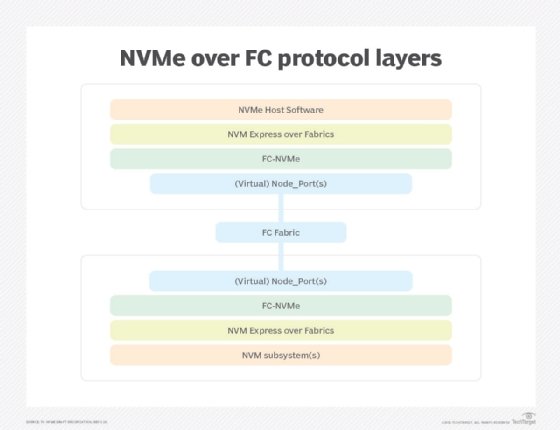
Nonvolatile memory express over Fibre Channel (NVMe over FC) -- which is implemented through the Fibre Channel-NVMe (FC-NVMe) standard -- is a technology specification designed to enable NVMe-based message commands to transfer data and status information between a host computer and a target storage subsystem over a Fibre Channel network fabric.
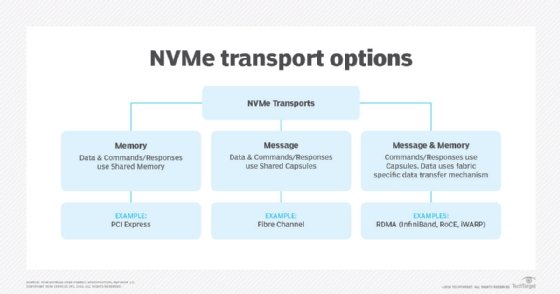
Fibre Channel is a fabric transport option for NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF), a specification developed by NVM Express Inc., a nonprofit organization with more than 100 member technology companies. Additional NVMe transport options include remote direct memory access (RDMA) over Ethernet and InfiniBand. NVM Express Inc. published the 1.0 version of NVMe-oF on June 5, 2016.
The T11 committee of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS) defined a frame format and mapping protocol to apply NVMe-oF to Fibre Channel. The T11 committee finalized the first version of the FC-NVMe standard in August 2017 and submitted it to INCITS for publication.
How NVMe over FC works
The FC Protocol (FCP) allows the mapping of upper-layer transport protocols, such as NVMe, Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) and IBM's proprietary Fibre Connection (Ficon), on top of it to enable the transfer of data and commands between a host computer and a peripheral target storage device or system.
In comparison to SCSI and FICON, NVMe has a streamlined register interface and command set, reduces the input/output (I/O) stack's CPU overhead, lowers latency and improves performance. NVM Express Inc. developed NVMe for use with fast media, including solid-state drives (SSDs) and other memory-based technologies. By contrast, the SCSI command set was designed at a time when slower hard disk drives (HDDs) and tape were the primary storage media, and FICON was created to connect mainframe computer and storage devices.
FC-NVMe simplifies the NVMe command sets into basic FCP instructions. Because Fibre Channel is designed for storage traffic, functionality such as discovery, management and end-to-end qualification of equipment is built into the system.
A major distinction between NVMe-oF, including NVMe over Fibre Channel, and NVMe is the mechanism for transporting commands. NVMe maps requests and responses to shared memory in the host computer via the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) interface protocol. NVMe-oF uses a message-based model to send requests and responses between a host and a target storage device over a network.
NVMe-oF facilitates the use of alternative transports to PCIe to expand the distance over which an NVMe host and an NVMe storage subsystem can communicate. The initial design goal for NVMe-oF was to add no more than 10 microseconds of latency between the NVMe host and NVMe storage target, connected over a suitable network fabric, in comparison to the latency of an NVMe storage device using a local host's PCIe bus.
Large-scale block flash-based storage environments that use Fibre Channel are the most likely to adopt NVMe over FC. FC-NVMe offers the same structure, predictability and reliability characteristics for NVMe-oF that Fibre Channel does for SCSI. Plus, NVMe-oF traffic and traditional SCSI-based traffic can run simultaneously on the same FC fabric.
Infrastructure components that must support NVMe over Fibre Channel to enable the potential benefits include the storage operating system (OS) and network adapter cards. FC storage system vendors must qualify FC-NVMe with their products. Vendors with host bus adapters (HBAs) that support FC-NVMe include Broadcom and Cavium. Broadcom and Cisco are the major FC switch vendors.
FC-NVMe advantages and disadvantages
FC-NVMe offers the advantages of higher performance, reduced latency and parallel I/O in transferring data to and from SSDs using the NVMe command set, in comparison to data transfer with the SCSI command set to and from HDDs or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) or Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) SSDs. One disadvantage of NVMe-based SSDs may be higher cost, but the price of NVMe SSDs is expected to reach parity with some types of traditional SSDs.
Comparing FC-NVMe to Ethernet- or InfiniBand-based NVMe-oF alternatives generally takes into consideration the advantages and disadvantages of the networking technologies. Fibre Channel fabrics are noted for their lossless data transmission, predictable and consistent performance, and reliability. Large enterprises tend to favor FC storage for mission-critical workloads. But Fibre Channel requires special equipment and storage networking expertise to operate and can be more costly than Ethernet-based alternatives.
Ethernet-based NVMe storage products tend to be more plentiful then FC-NVMe-based options. Most storage startups focus on Ethernet-based NVMe and sometimes incorporate proprietary technology to get their products to market faster.
InfiniBand-based NVMe tends to hold appeal for high-performance computing workloads requiring exceptionally high bandwidth and low latency. InfiniBand networks are typically used for communication within back-end storage systems, rather than host-to-storage communication. Like FC, InfiniBand is a lossless network requiring special hardware, and it offers advantages such as flow and congestion control, as well as quality of service (QoS). Unlike FC, InfiniBand and Ethernet lack a discovery service that enables the automatic addition of nodes to the fabric.
The NVMe-oF specification supports RDMA, with mappings including RDMA over converged Ethernet (RoCE) and Internet Wide-area RDMA Protocol (iWARP) for Ethernet and InfiniBand. The NVMe Express organization also plans to support a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) transport option.







